▏Product Vedio
▏Laboratory Plastic Extruder
▏Introduction to Laboratory Plastic Extruder
The Laboratory Plastic Extruder is an advanced and compact system designed for small-scale plastic processing. It plays a critical role in polymer research, material testing, and product development in laboratories, academic institutions, and R&D facilities. This high-precision equipment is ideal for experimenting with new plastic formulations, testing material properties, and creating prototypes before scaling up to full-scale production.
Laboratory plastic extruders are widely used in the production of various thermoplastic products such as films, sheets, pipes, profiles, and other polymer-based components. They offer controlled extrusion conditions, allowing manufacturers and researchers to examine the physical and chemical properties of polymers, ensuring that the final products meet specific quality standards. Whether working with thermoplastics like PVC, PE, or PP, the laboratory extruder provides an efficient and reliable solution for processing materials in a research and development setting.
▏Key Features of the Laboratory Plastic Extruder

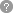 | High-Precision Extrusion for Polymer Processing |
| One of the key features of the Laboratory Plastic Extruder is its ability to perform precise and consistent extrusion. This is crucial when dealing with small quantities of material, as even slight variations in temperature, pressure, or screw speed can affect the final product's properties. The extruder is designed to maintain a stable processing environment, ensuring that the material is melted and shaped under optimal conditions.
The extruder typically includes a specialized screw and barrel system that allows for the smooth processing of different types of thermoplastics. By controlling the temperature and screw speed, researchers can fine-tune the process to achieve the desired material characteristics, such as melt flow index, tensile strength, and flexibility. |
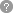 | Versatile Processing Capabilities |
|
Temperature control is a critical factor in the extrusion process, especially when dealing with sensitive polymer materials. The Laboratory Plastic Extruder is equipped with advanced digital temperature controllers that provide precise control over the extrusion temperature. Multiple temperature zones along the barrel and die ensure that the material is processed at the ideal temperature throughout the entire process. Accurate temperature regulation helps avoid overheating or underheating, which can lead to polymer degradation or inconsistent material properties. By maintaining a stable temperature profile, researchers can achieve the exact material characteristics they require for their tests or prototypes. |
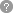 | Precision Temperature Control |
|
Temperature control is a critical factor in the extrusion process, especially when dealing with sensitive polymer materials. The Laboratory Plastic Extruder is equipped with advanced digital temperature controllers that provide precise control over the extrusion temperature. Multiple temperature zones along the barrel and die ensure that the material is processed at the ideal temperature throughout the entire process.
Accurate temperature regulation helps avoid overheating or underheating, which can lead to polymer degradation or inconsistent material properties. By maintaining a stable temperature profile, researchers can achieve the exact material characteristics they require for their tests or prototypes. |
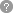 | Compact and Space-Efficient Design |
|
The Laboratory Plastic Extruder is designed with a compact footprint, making it ideal for laboratory settings where space is limited. Despite its small size, it provides the same level of precision and functionality as larger, industrial-scale extruders. This space-efficient design allows labs to maximize their available workspace without sacrificing performance.
Its portability also makes it easy to move between different research areas or integrate into existing workflows. Whether used for single-project runs or continuous testing, the Laboratory Plastic Extruder is versatile and adaptable for various laboratory environments. |
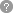 | Enhanced Cooling and Shaping Systems |
|
Once the polymer is extruded, it must be cooled quickly to retain its shape and ensure the desired material properties. The Laboratory Plastic Extruder is equipped with an effective cooling system that can include air cooling or a water bath, depending on the material being processed. The rapid cooling process ensures that the material maintains its dimensional accuracy and surface quality, which is critical for many applications.
Additionally, the extruder often features a die that allows for shaping the extruded material into different profiles or geometries. Customizable dies enable researchers to create specific shapes or cross-sections, making it easier to produce prototypes for testing and analysis. |
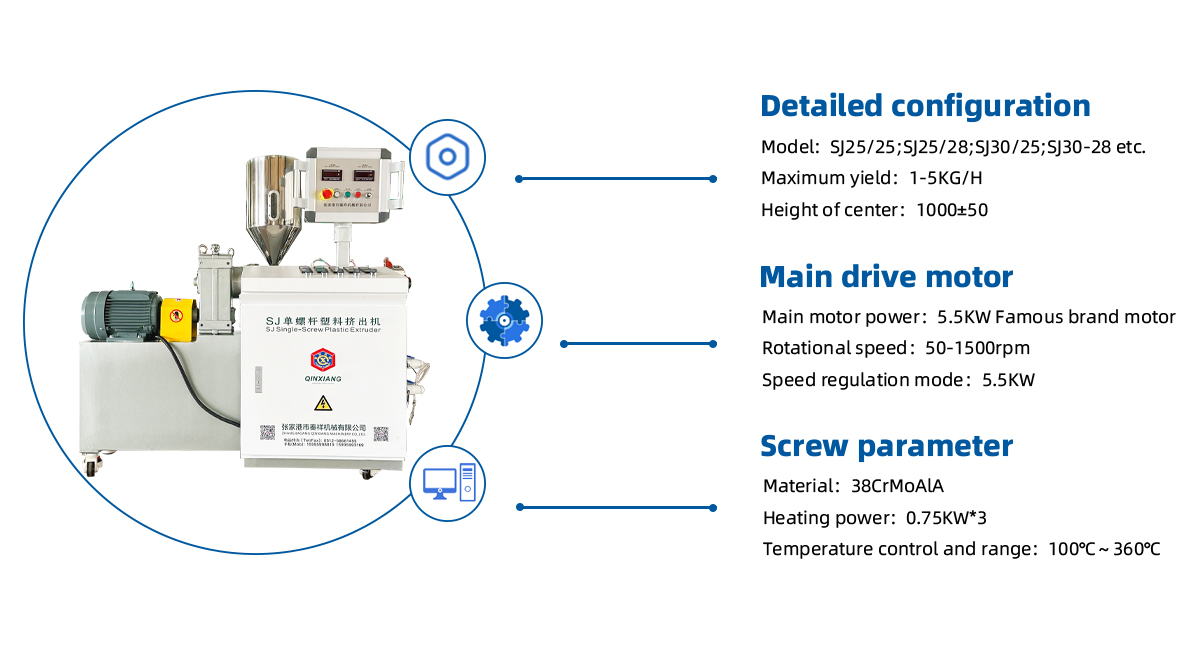
▏Main Details
▏Product Photos
▏How the Laboratory Plastic Extruder Works

 | Material Feeding and Plasticization |
| The extrusion process begins with the feeding of raw plastic materials, which are typically in pelletized or powdered form, into the extruder’s hopper. The material is then conveyed by the rotating screw into the barrel, where it is heated and plasticized. The screw design ensures that the material is evenly heated and melted, forming a homogeneous melt ready for extrusion.
Precise temperature control in the barrel ensures that the material reaches the desired melt viscosity for easy shaping. The speed of the screw is adjustable, allowing for precise control over the material flow rate. |
 | Extrusion and Shaping |
|
As the molten plastic material flows from the barrel, it is forced through a die to create the desired shape. The die is customized to produce specific profiles, such as pipes, sheets, or films, depending on the research requirements. The Laboratory Plastic Extruder can accommodate a wide variety of dies, allowing for the production of different extruded products for experimentation.
The pressure and flow rate are carefully controlled during the extrusion process to maintain consistent material dimensions and quality. The system can be adjusted to accommodate various processing conditions and formulations, ensuring flexibility in product development. |
 | Cooling and Solidification |
|
Once the material exits the die, it is rapidly cooled to solidify its shape. The cooling process is essential to prevent deformation and to retain the material’s dimensional accuracy. Cooling methods can vary based on the type of material and the product’s requirements. For example, air cooling is often used for films and sheets, while water baths are ideal for more rigid profiles.
By controlling the cooling rate, researchers can influence the material's properties, such as strength, flexibility, and surface finish. This control over the cooling phase is important for experimenting with different material formulations. |
 | Cutting and Sampling |
|
After the material has cooled and solidified, it is cut into the desired lengths for sampling, further analysis, or testing. The cutting system is integrated into the extruder and provides precision cuts, ensuring that the samples meet the exact specifications required for testing.
Automated cutting allows for continuous production without the need for manual intervention, making the process more efficient and reducing the potential for errors. The samples are then ready for further analysis, quality control checks, or use in prototype development. |
▏Applications of the Laboratory Plastic Extruder

 | 1. Material Research and Development
The Laboratory Plastic Extruder is an essential tool for material researchers, offering the ability to experiment with different polymer blends, additives, and formulations. Whether working with basic thermoplastics or creating more complex composite materials, the extruder provides the precision needed to test and refine new polymer-based compounds. 2. Prototyping and Product DevelopmentManufacturers in industries such as automotive, medical, and packaging use the Laboratory Plastic Extruder to create prototype products for testing and evaluation. By producing small-scale extrusions of pipes, films, or profiles, researchers can assess the material's performance before moving to larger-scale production. This process helps reduce risks and costs associated with scaling up production. 3. Educational and Training PurposesThe Laboratory Plastic Extruder is also widely used in educational settings to teach students and trainees the principles of polymer processing. It provides hands-on experience in extrusion technology, offering valuable insights into the challenges and nuances of working with thermoplastics. 4. Quality Control and TestingFor companies involved in manufacturing plastic products, the Laboratory Plastic Extruder can be used to produce test samples for quality control. This allows manufacturers to test the properties of their materials before large-scale production, ensuring that the final product meets regulatory standards and customer expectations. |
▏Advantages of the Laboratory Plastic Extruder
 | 1. Precise Control Over Extrusion Parameters
The Laboratory Plastic Extruder offers precise control over critical extrusion parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and screw speed. This allows researchers to fine-tune the process to achieve the desired material properties. 2. Compact and Efficient DesignWith its compact design, the Laboratory Plastic Extruder is ideal for small-scale production, R&D, and testing purposes. It occupies less space compared to larger, industrial machines, making it perfect for laboratories with limited space. 3. Versatility for Different ApplicationsWhether you are working with different types of thermoplastics, producing various profiles, or testing new formulations, the Laboratory Plastic Extruder offers the versatility needed for a wide range of applications. 4. Cost-Effective SolutionThe Laboratory Plastic Extruder provides a cost-effective way to conduct small-scale production and testing, reducing the need for expensive full-scale extrusion lines. It allows for experimentation and prototyping without the significant financial investment required for larger machinery. |
▏Innovation and Precision at Your Fingertips
The Laboratory Plastic Extruder offers researchers, manufacturers, and educational institutions a precise, versatile, and efficient tool for plastic processing. Whether used for R&D, testing, or prototyping, this extruder provides the capabilities needed to create high-quality polymer products on a small scale. With its advanced control systems, compact design, and ability to handle a wide range of thermoplastics, the Laboratory Plastic Extruder is an invaluable asset for anyone involved in the development and testing of new plastic materials.
▏About Us

▏Corporate Culture

▏Cooperative Parts Supplier

▏Packing And Shipping